概述
不同于手机端,TV端一般是16:9横屏且屏幕较大,因此在TV端的设计中很难看到单行/单列的列表布局,一般都是3~4列的纵向列表或者3~4行的横向列表,今年市面上主流的TV端设计是以3~4列纵向列表为主,在向下滚动时,焦点item滚动到屏幕内垂直居中,比如下图中的斗鱼TV端。
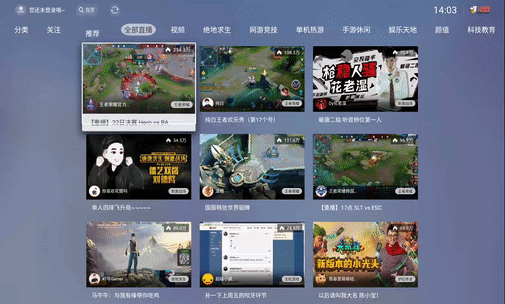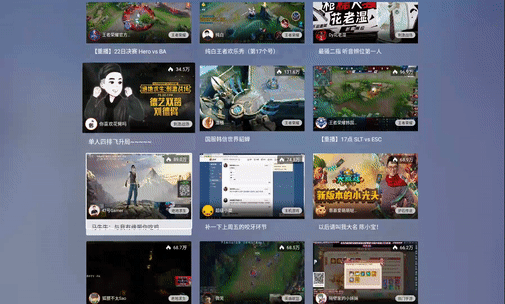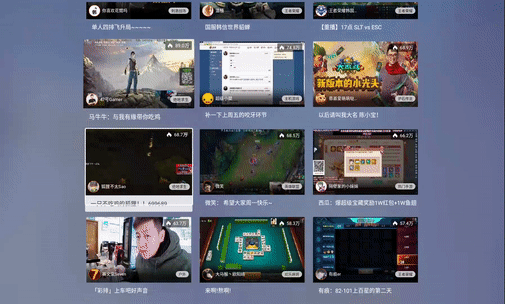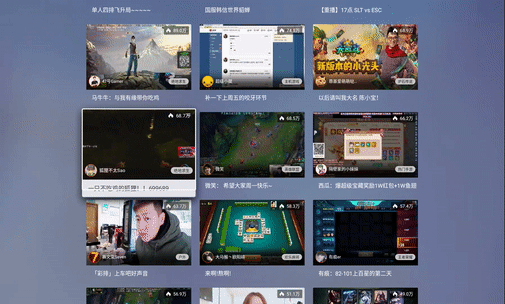
由于手机端触屏不存在这样的交互方法,所以我们必须针对TV端设计通用实现。
ScrollView实现方法
ScrollView提供了一个方法去计算从从一个焦点跳到下一个焦点需要滚动的delta值:computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen()
这个方法是protected的,我们要做的就是自定义一个ScrollView,重写此方法,将滚动到终点的偏移量加入进去
public class TVScrollView extends NestedScrollView {
...
protected int computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(Rect rect) {
if (getChildCount() == 0) return 0;
int height = getHeight();
int screenTop = getScrollY();
int screenBottom = screenTop + height;
int fadingEdge = getVerticalFadingEdgeLength();
// leave room for top fading edge as long as rect isn't at very top
if (rect.top > 0) {
screenTop += fadingEdge;
}
// leave room for bottom fading edge as long as rect isn't at very bottom
if (rect.bottom < getChildAt(0).getHeight()) {
screenBottom -= fadingEdge;
}
int scrollYDelta = 0;
Rect currentRect = new Rect();
if (findFocus() != null) {
offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(findFocus(), currentRect);
}
if (rect.top > currentRect.top && rect.bottom > currentRect.bottom) {
// need to move down to get it in view: move down just enough so
// that the entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first
// screen size chunk).
if (rect.height() > height) {
// just enough to get screen size chunk on
scrollYDelta += (rect.top - screenTop);
} else {
// get entire rect at bottom of screen
scrollYDelta += (rect.bottom - screenBottom);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling beyond the end of our content
int bottom = getChildAt(0).getBottom();
int distanceToBottom = bottom - screenBottom;
scrollYDelta = Math.min(scrollYDelta, distanceToBottom);
// 在这里加上滚动到parent中部的偏移量 delta = (parent height - view height) / 2
scrollYDelta += (getHeight() - rect.height()) / 2;
}
else if (rect.top < currentRect.top && rect.bottom < currentRect.bottom) {
// need to move up to get it in view: move up just enough so that
// entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first screen
// size chunk of it).
if (rect.height() > height) {
// screen size chunk
scrollYDelta -= (screenBottom - rect.bottom);
} else {
// entire rect at top
scrollYDelta -= (screenTop - rect.top);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling any further than the top our content
scrollYDelta = Math.max(scrollYDelta, -getScrollY());
// 在这里加上滚动到parent中部的偏移量 delta = (parent height - view height) / 2
scrollYDelta -= (getHeight() - rect.height()) / 2;
}
// 此处为一个特殊的兼容处理,在某些情况下焦点选择到处于ScrollView顶部的View时,
// 会出现差几个像素没滚动到顶部的情况,导致偶现卡焦点,所以在这里直接将ScrollView
// 滚动到顶部避免此情况。
if (rect.top < (getBottom() / 2)) {
scrollYDelta = 0;
smoothScrollTo(0, 0);
}
return scrollYDelta;
}
......
}
在使用时直接使用这个TVScrollView便可实现焦点View垂直居中效果,此处只是举例实现方案,当然你也可以把这个“TVScrollView”写的更复杂,设定一些开关以实现不同的滚动效果。
RecyclerView的实现方法
相比于ScrollView不得不重写自定义控件,RecyclerView则要灵活很多。
追踪RecyclerView的源码可知RecyclerView的滚动效果是由设定在RecyclerView中的LayoutManager决定的
// 在RecyclerView的源码中,scrollTopPosition和smoothScrollToPosition都是直接调用LayoutManager对应的方法
// code in RecyclerView.java
public void scrollToPosition(int position) {
if (mLayoutFrozen) {
return;
}
stopScroll();
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot scroll to position a LayoutManager set. " +
"Call setLayoutManager with a non-null argument.");
return;
}
mLayout.scrollToPosition(position);
awakenScrollBars();
}
public void smoothScrollToPosition(int position) {
if (mLayoutFrozen) {
return;
}
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot smooth scroll without a LayoutManager set. " +
"Call setLayoutManager with a non-null argument.");
return;
}
mLayout.smoothScrollToPosition(this, mState, position);
}
我们要做的就是在LayoutManager上做点文章,RecyclerView库为我们提供了LinearSmoothScroller类去实现线性滑动效果,我们只需继承此类,根据需求在重写方法中计算滑动delta值,然后复写LayoutManager的scroll相关方法即可。
我以常见的GridLayoutManager为例:
public class CenterScrollGridLayoutManager extends GridLayoutManager {
private Context context;
private boolean isInLayout;
private boolean isScrolling;
/* ... constructors... */
public void smoothScrollToCenter(int position) {
isScrolling = true;
RecyclerView.SmoothScroller smoothScroller = new CenterScroller(context);
smoothScroller.setTargetPosition(position);
startSmoothScroll(smoothScroller);
isScrolling = false;
}
@Override
public void smoothScrollToPosition(RecyclerView recyclerView, RecyclerView.State state, int position) {
smoothScrollToCenter(position);
}
// 关键方法 - 焦点改变时触发滚动
@Override
public boolean onRequestChildFocus(RecyclerView parent, View child, View focused) {
if (!isInLayout && !isScrolling) {
smoothScrollToCenter(getPosition(child));
}
return true;
}
// 重写此方法用于在数据加载完成时触发滚动到中部
@Override
public void onLayoutChildren(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
isInLayout = true;
try {
super.onLayoutChildren(recycler, state);
if (getFocusedChild() != null && !isScrolling) {
if (getChildCount() - getPosition(getFocusedChild()) >= getSpanCount()) {
smoothScrollToCenter(getPosition(getFocusedChild()));
}
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ignored) {}
isInLayout = false;
}
// 自定义滚动效果的Scroller
private class CenterScroller extends LinearSmoothScroller {
private static final float MILLISECONDS_PER_INCH = 50f; //default is 25f (bigger = slower)
public CenterScroller(Context context) {
super(context);
}
// 这里计算滚动到中部的偏移量
@Override
public int calculateDtToFit(int viewStart, int viewEnd, int boxStart, int boxEnd, int snapPreference) {
return (boxStart + (boxEnd - boxStart) / 2) - (viewStart + (viewEnd - viewStart) / 2);
}
// 滚动速度控制
@Override
protected float calculateSpeedPerPixel(DisplayMetrics displayMetrics) {
return MILLISECONDS_PER_INCH / displayMetrics.densityDpi;
}
}
}
这样,使用此LayoutManager的RecyclerView自带焦点垂直居中的效果。LinearLayoutManager实现同理,可以看到RecyclerView的灵活性和可扩展性都是相当强的。
ListView、GridView等布局
使用RecyclerView替换~~
都8102年了,重构页面还用ListView这种局部刷新都费劲的古董干啥呀……